How to Create a Distinctive Lo-Fi Sound
Lo-fi can be difficult to define. It’s typically something you can identify once you hear it.
Simply put, lo-fi is a production sound or style opposite to what we perceive to be a high quality recording.
Since recording technology is changing, and we base our notion of high definition on the recording technology of the time, what is lo-fi must too be changing.
What lo-fi is today may have been the hi-fi of 30 years ago. With that in mind, it is always best to think of lo-fi, as that which either no longer fits into the notion of high-fidelity, or that which emulates the sound of past technologies.
With a definition that expansive, creating a lo-fi sound can mean many different things.
Follow the example below to create a lo-fi sound, but know that a lo-fi sound can be accomplished in more ways than detailed here.
Equalization:
A full frequency response is something we’ve become accustomed to in modern recording. By narrowing the frequency response of an instrument or full mix, we’ve taken the first step to create a lo-fi sound.
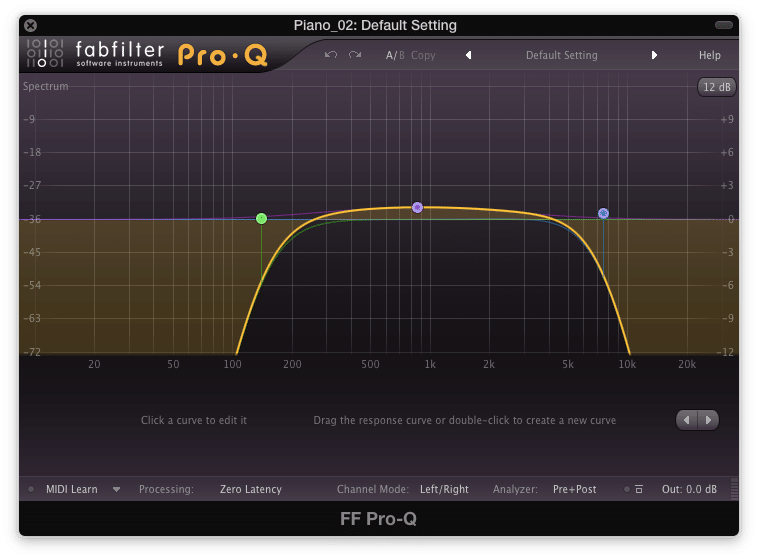
Use an EQ to create a narrow frequency response
Step 1: Insert an EQ. Using a high pass filter, cut up until roughly 200Hz. Using a low pass filter, cut down to roughly 6500Hz.
Step 2: Boost the midrange of the recording, using a wide Q, to accomplish a vintage sound.
The numbers listed above are subjective, and should be changed to personal taste.
Distortion:
Digital Distortion:
The Goodhertz Lossy, allows for digital distortion. Unlike with equalization, we aren’t trying to emulate classic technology, but instead separate our sound even further from the notion of high fidelity.
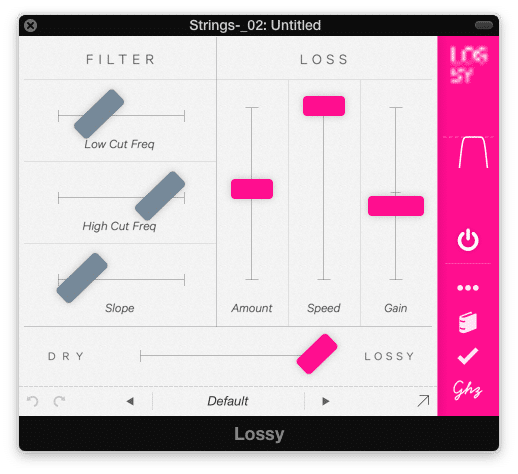
This unique plugin allows for digital distortion - an effect rarely used, but great for lo-fi mixing
This plugin introduces aliasing, while reducing the bit depth and sampling rate of the song. This results in audio degradation that is distinctly digital.
For this plugin, I don’t suggest using any particular settings; however, I would suggest using this plugin in a noticeable way. To ensure that, I slide the “dry lossy’ fader to lossy.
Analog Distortion:
Tape emulation is great way to create both tape and tube distortion - both of which parallel past recording technology.
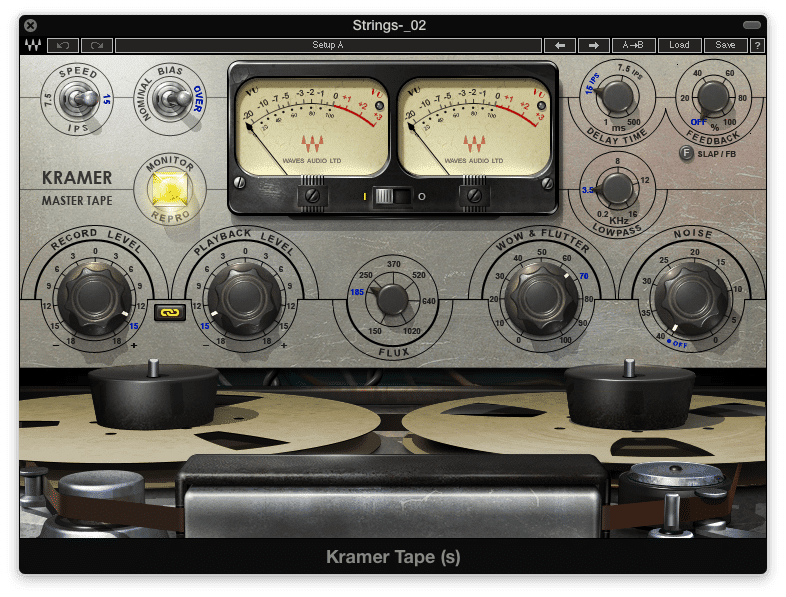
Tape emulation allows for tape and tube distortion - along with flutter, noise, and an eq cut caused by a slower tape speed
Step 1: The quickest way to accomplish distortion with a tape emulator is to boost the input significantly, while reducing the output significantly. This results in an overdriven sound, with harmonic distortion.
Step 2: Increase the flux knob to change the magnetic flux emulation of the tape. Increasing this knob results in both tape distortion, and tube distortion.
Step 3: Adjust the noise, flutter, and tape speed to personal taste. Each option can degrade the signal farther, creating a lo-fi sound.
Conclusion:
Although the definition of lo-fi is less grounded than most audio terms, understanding it in context with high fidelity recordings is key to creating it. Again, it truly is doing anything to create a sound, other than that of a high definition modern recording. As recording technology changes, what is hi-fi and lo-fi will change as well. Research the sound of classic recordings and technologies for inspiration and ideas.
How do you create a lo-fi sound?




